Minimal Invasive Spine Surgery
Conventional Spine Surgery involves taking long incisions, forceful muscle retraction for prolonged time, removal of normal tissues like ligaments and bone to approach area of pathology. Most of the times these surgeries are done under prolonged general anesthesia.
This long incisions and injury to normal structures results in
- Increased blood loss
- Increased scar tissue formation
- Increased chance of neural injury
- Epidural scarring
- Denervation of paraspinal muscles
- Delayed Mobility
- Longer Hospitalisation Stay
- All these cause increased morbidity.
Minimal Invasive Spine Surgery involves
- Muscle Splitting Approach
- Minimal muscle retraction
- Less normal tissue damage
- Small Incision
- Less Blood Loss
- Early Mobilisation
- Preservation of muscle
- Paraspinal Muscle attachment preserved
- Less hospital Stay
- Targeted treatment of pathology
Advantages:-
- Many surgeries are done under local anesthesia, hence surgeries can be done even in patients with high risk of anesthesia
- There is less blood loss
- Minimal morbidity
- Patient can be mobilized very early and he can be back to work faster
- It prevents complications associated with prolonged bed rest
- Less neural tissue damage
Since normal tissues are not removed or damaged, post operative pain is less and also there is less chance of failed back syndrome. To achive these objectives many advanced instruments like Microscope, Endoscope, Radio-frequency and Laser spectal less tissue damaging retractions
Types
Note:- All images are copyrighted and require proper licensing or permission for use. Unauthorized use is prohibited.
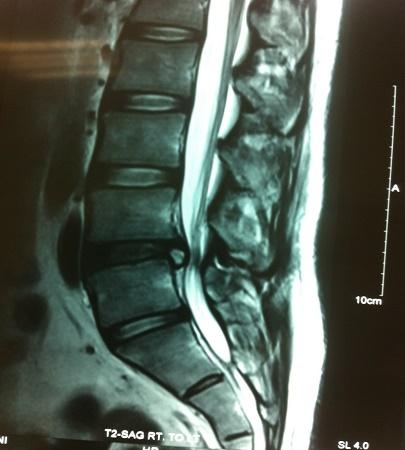
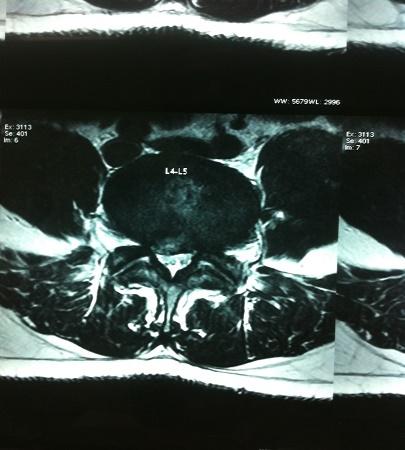
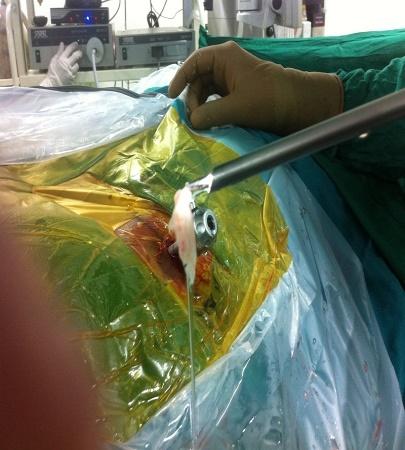
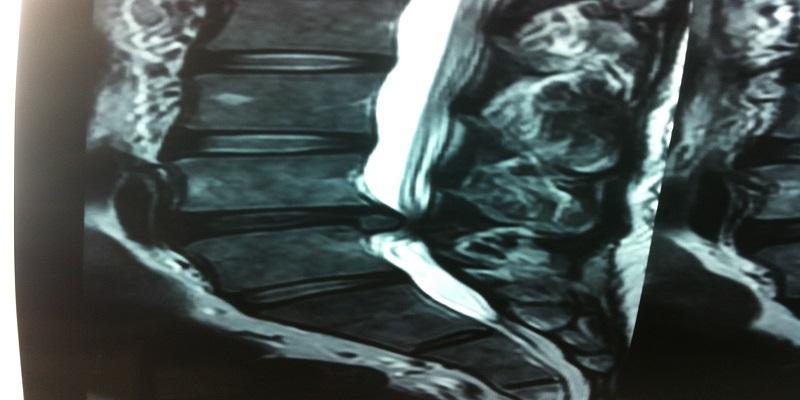
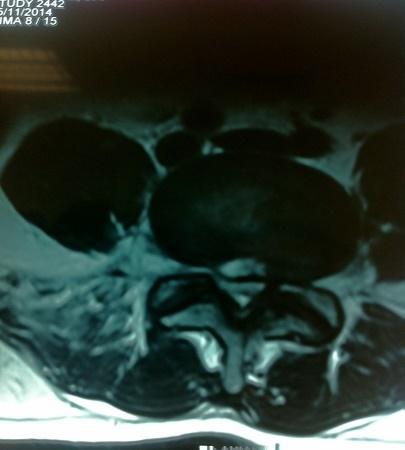
Percutaneous Endoscopic Lumbar Discectomy
This is a unique type of surgery performed for prolapsed intervertebral discs. It is a truly minimally invasive spine surgery conducted using the YESS scope and performed under local anesthesia with conscious sedation. An endoscope is passed transforaminally into the affected disc under local anesthesia, and targeted fragmentectomy is carried out. The wound is closed with a single stitch. Patients are mobilized and can typically be discharged the same day.
- Surgery performed under local anesthesia with conscious sedation
- 0.5 cm skin incision
- Endoscope used for surgery
- No damage to muscles, ligaments, or normal tissues
- Targeted fragmentectomy: Direct removal of the prolapsed disc tissue
- No blood loss
- Same-day discharge
- No prolonged bed rest required after surgery: Patients can resume work sooner.
- Effective for various cases: Prolapsed, migrated, extraforaminal, and recurrent discs can be treated.
- Ideal for elderly and medically compromised patients: A highly suitable and safe technique.
Note:- All images are copyrighted and require proper licensing or permission for use. Unauthorized use is prohibited.
MED / METRx Tubular Retractor
- Technique similar to microdiscectomy
- Paramedian muscle-splitting approach: Preserves muscle integrity.
- Serial dilators used: Splits muscles without causing damage.
- Enhanced visualization: Magnification and illumination provided by a microscope or endoscope.
Advantages of Tubular Retraction
- Paramedian approach: Muscle is not detached from its attachments.
- No muscle ischemia
- No muscle scarring
- Minimal to negligible bleeding
- Targeted treatment: Focused on the specific area of pathology.
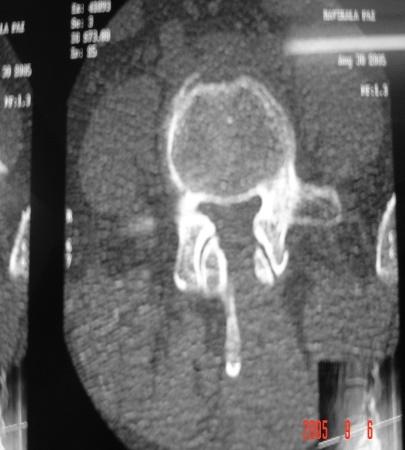
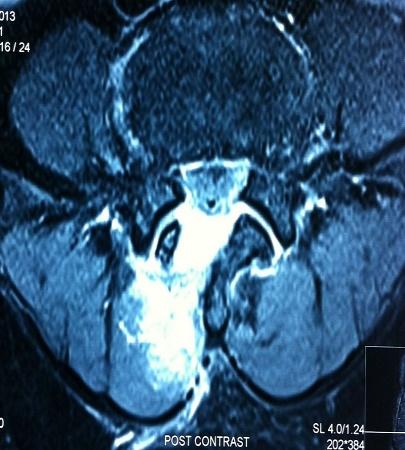
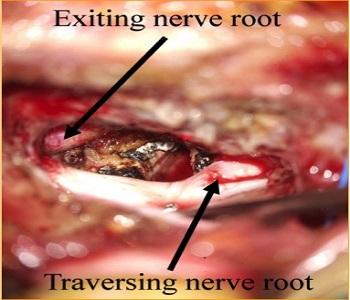
MED / Microdecompression
Surgery Cases
- Useful for treating all types of disc prolapse.
- Effective for intervertebral disc prolapse causing root compression with radiculopathy/sciatica.
- Beneficial for lumbar canal stenosis with associated leg pain.
- Unilateral approach with bilateral foraminotomy.
- Minimal blood loss.
- Same-day mobilization.
- Discharge within 2-3 days.
- Superior to microdiscectomy.
Note:- All images are copyrighted and require proper licensing or permission for use. Unauthorized use is prohibited.
Note:- All images are copyrighted and require proper licensing or permission for use. Unauthorized use is prohibited.
Note:- All images are copyrighted and require proper licensing or permission for use. Unauthorized use is prohibited.
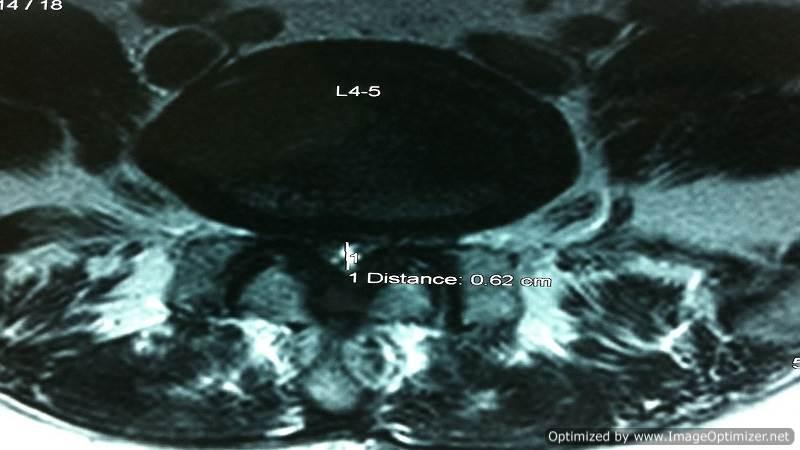
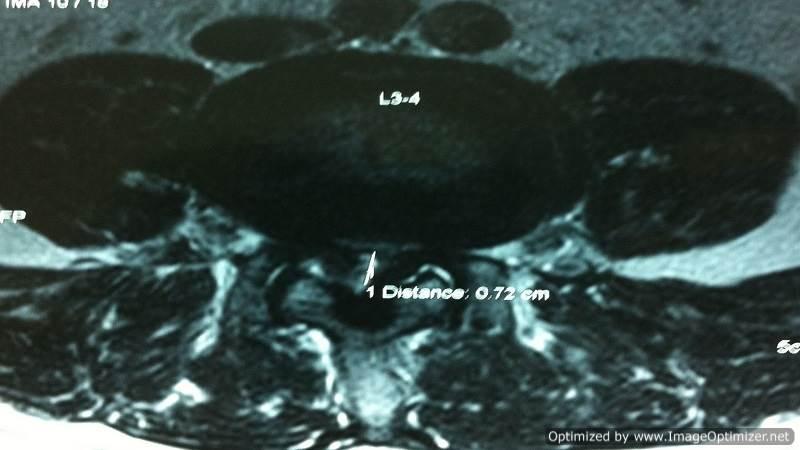
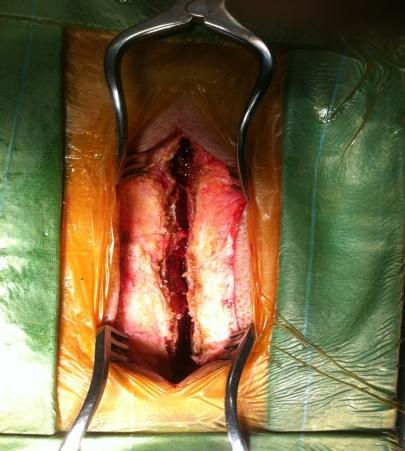
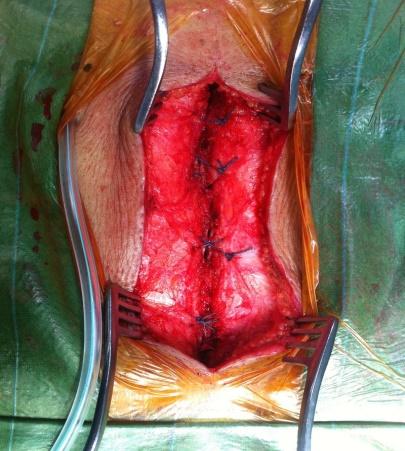
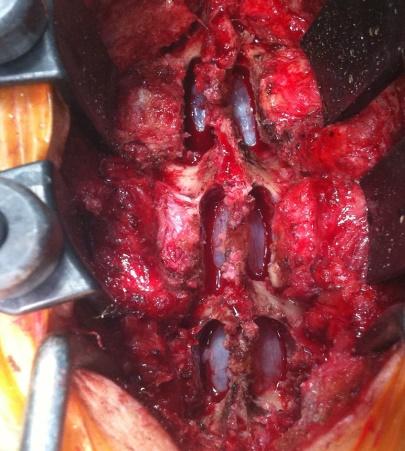
SpS Microdecompression
In cases of multilevel degenerative canal stenosis without instability and with medical comorbidities, we prefer spinous process-splitting microdecompression, a method developed by our team:
- Spinous process split in the middle: Muscle attachments are preserved and not disturbed.
- Decompression performed using a microscope: Ensures precision and minimizes collateral damage.
- Normal anatomy restored: Maintains structural integrity at the end of surgery.
- Muscle attachments preserved: Reduces post-operative pain and improves recovery.
- Fusion avoided: Preserves motion at the treated level.
- Can be combined with fusion surgery: If necessary, cortical screws can be used for stabilization.

Note:- All images are copyrighted and require proper licensing or permission for use. Unauthorized use is prohibited.
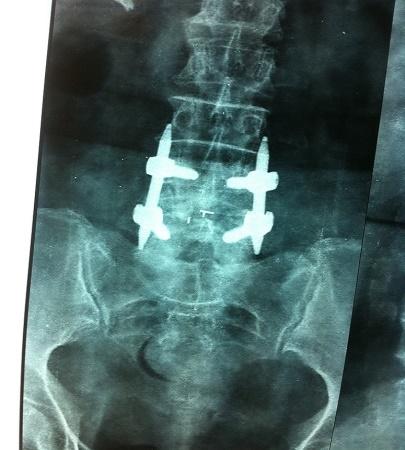
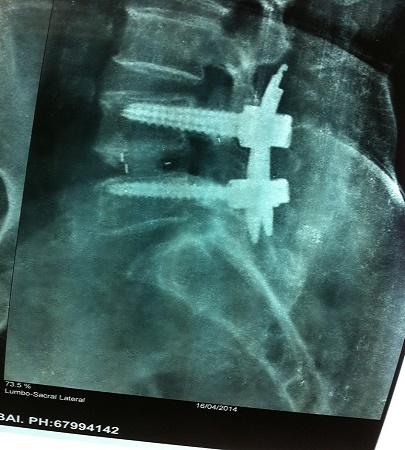
Fusion MISS TLIF
Spinal fusion may be necessary for various pathologies that cause spinal instability. In the lumbar spine region, I have been performing posterior lumbar interbody fusion (PLIF) surgeries using interbody cages with bone grafts and posterior stabilization with pedicle screw fixation.
With advancements in surgical techniques, I have refined the process by adopting Transforaminal Lumbar Fusion (MISS), a minimally invasive approach. This technique preserves the midline spinal structures and significantly reduces the risk of epidural scarring.
- Spinous process split in the middle: Muscle attachments are preserved and not disturbed.
- Decompression performed using a microscope: Ensures precision and minimizes collateral damage.
- Normal anatomy restored: Maintains structural integrity at the end of surgery.
- Muscle attachments preserved: Reduces post-operative pain and improves recovery.
- Fusion avoided: Preserves motion at the treated level.
- Can be combined with fusion surgery: If necessary, cortical screws can be used for stabilization.
- Fusion surgery assisted by a microscope: Ensures precision.
- Preservation of midline structures: Maintains anatomical integrity.
- Complete decompression of nerve roots: Effective pain relief.
- No epidural scarring: Promotes faster healing.
- Early postoperative recovery: Patients mobilize sooner with less discomfort.
- Minimized morbidity: Results in quicker and smoother recovery.
- Use of interbody cages and bone grafts.
- Preservation of midline structures.
- Percutaneous screw fixation: Minimizes tissue damage.
- Fixed tubular retractor: Allows a focused surgical approach.
- Small incision: Only 2.5 cm.
- No blood transfusion required.
- Rapid mobilization: Patients are able to move on the same day.
- Short hospital stay: Discharge in 3-4 days.
- Ideal for revision/failed back surgeries.
- Low morbidity: Ensures better patient outcomes.
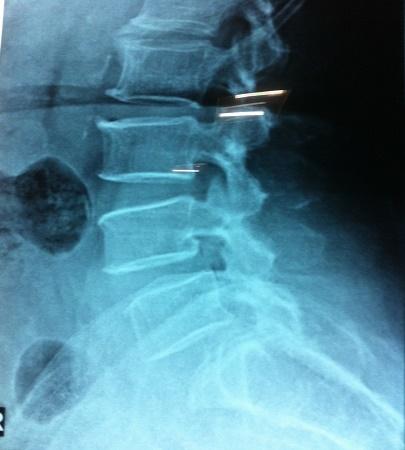
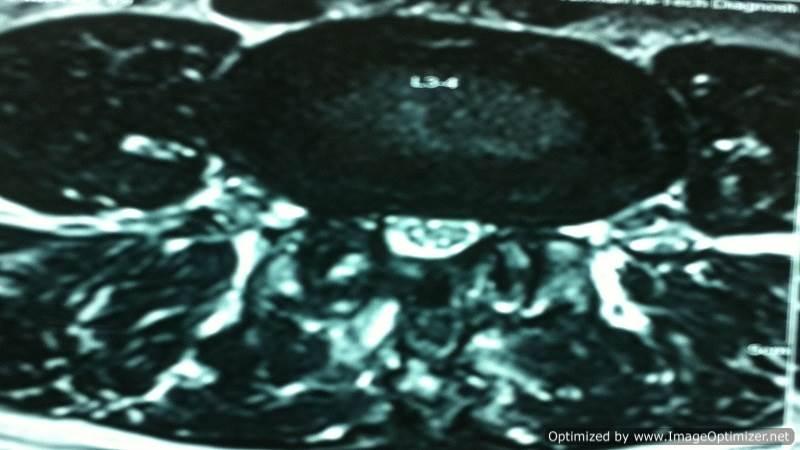
Note:- All images are copyrighted and require proper licensing or permission for use. Unauthorized use is prohibited.
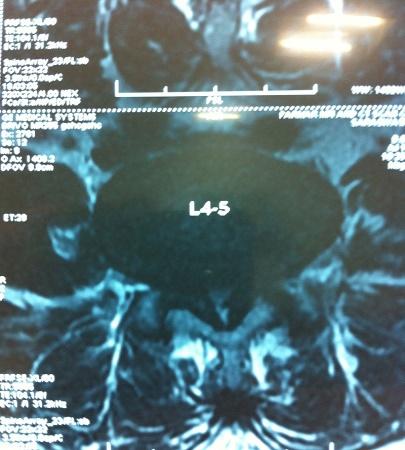
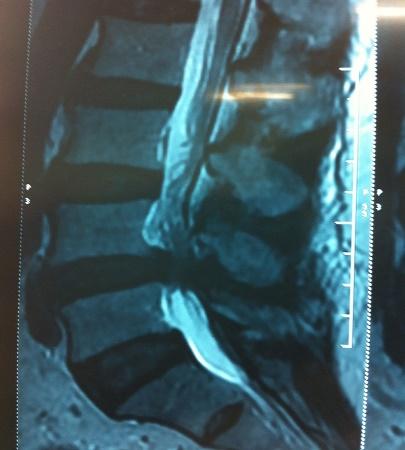
Note:- All images are copyrighted and require proper licensing or permission for use. Unauthorized use is prohibited.
Note:- All images are copyrighted and require proper licensing or permission for use. Unauthorized use is prohibited.
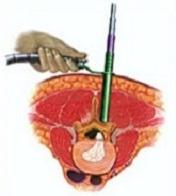
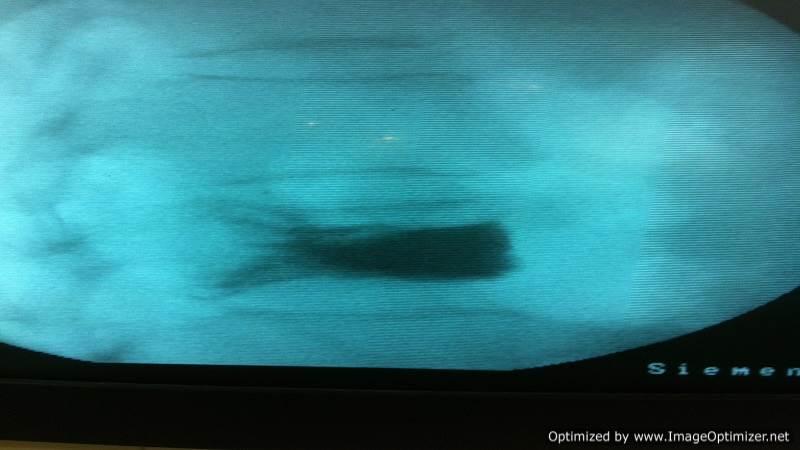
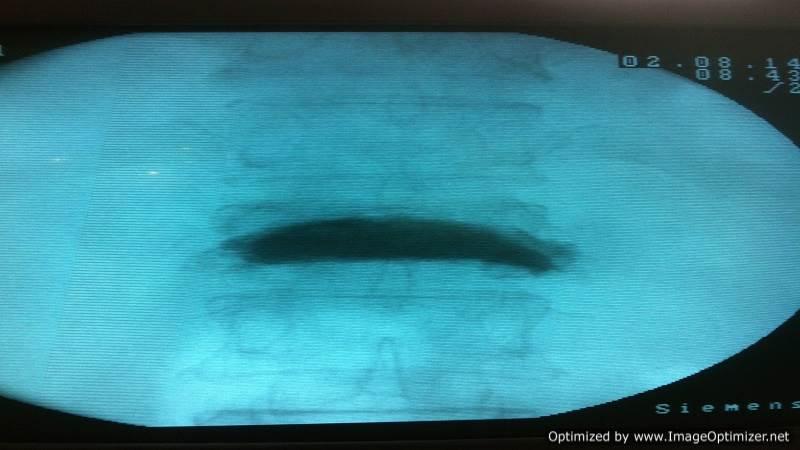
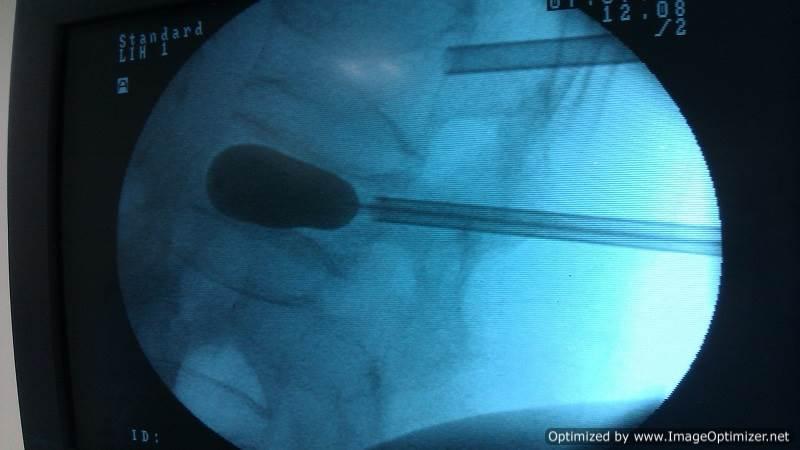
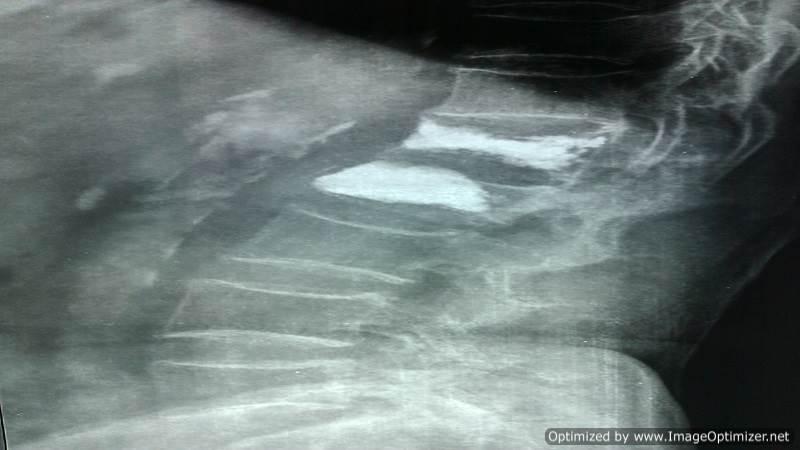
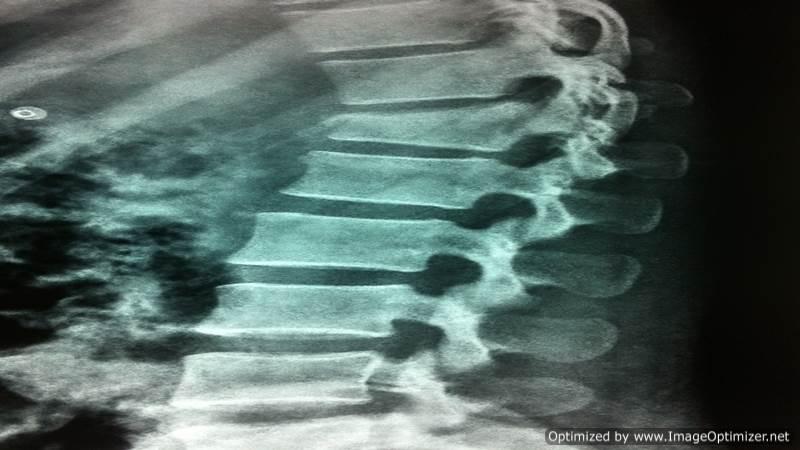
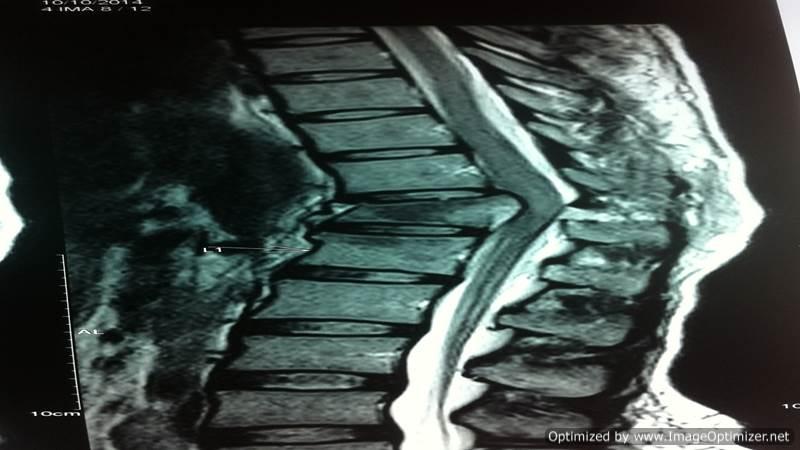
Vertebroplasty
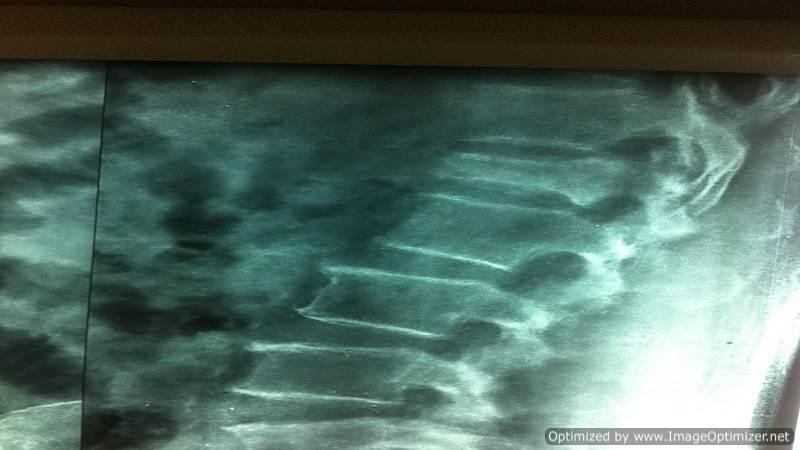
Osteoporotic Compression Fractures are a common occurrence in the elderly, even after minor trauma. Despite adequate conservative treatment, persistent pain from these fractures can lead to significant morbidity and disability.
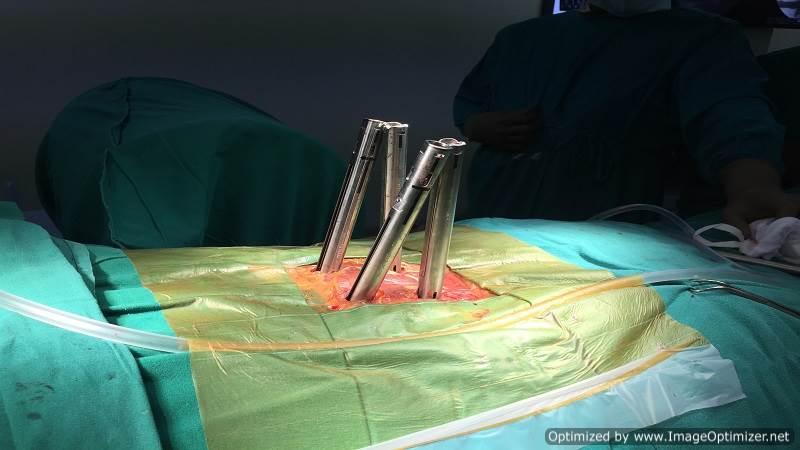
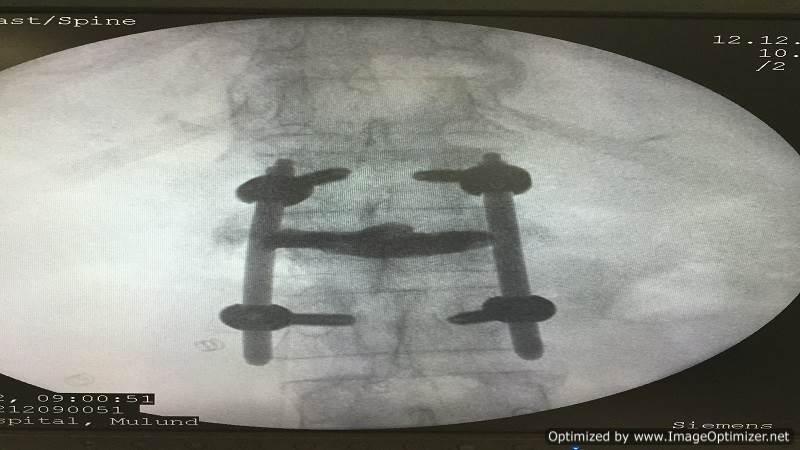
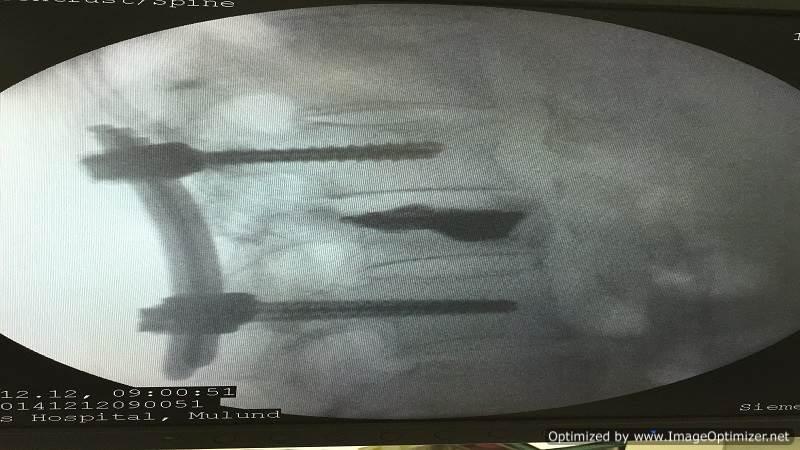
I perform vertebroplasty under local anesthesia with IITV (image intensifier) guidance. In this procedure, a specialized needle is inserted transpedicularly into the fractured vertebral body under local anesthesia, and bone cement is injected. Once hardened, the cement supports the fractured segment, providing immediate pain relief. This approach enables patients to mobilize immediately, reducing the morbidity and complications associated with prolonged bed rest. The same technique is effectively applied to treat painful metastatic bone fractures.
Key Features of Vertebroplasty:
- Effective for osteoporotic compression fractures and painful metastatic fractures.
- Immediate pain relief: Enhances patient comfort and recovery.
- Improves quality of life: Particularly for elderly patients.
- Daycare procedure: No prolonged hospitalization required.
In selected cases, I also perform balloon kyphoplasty, where the fractured, compressed vertebra is expanded to restore height before cement injection, offering additional structural benefits.
This minimally invasive approach provides a safe, effective solution for managing vertebral fractures, ensuring better outcomes and faster recovery for patients.

Note:- All images are copyrighted and require proper licensing or permission for use. Unauthorized use is prohibited.
Key Features of Vertebroplasty:

Note:- All images are copyrighted and require proper licensing or permission for use. Unauthorized use is prohibited.
Key Features of Vertebroplasty:
Note:- All images are copyrighted and require proper licensing or permission for use. Unauthorized use is prohibited.
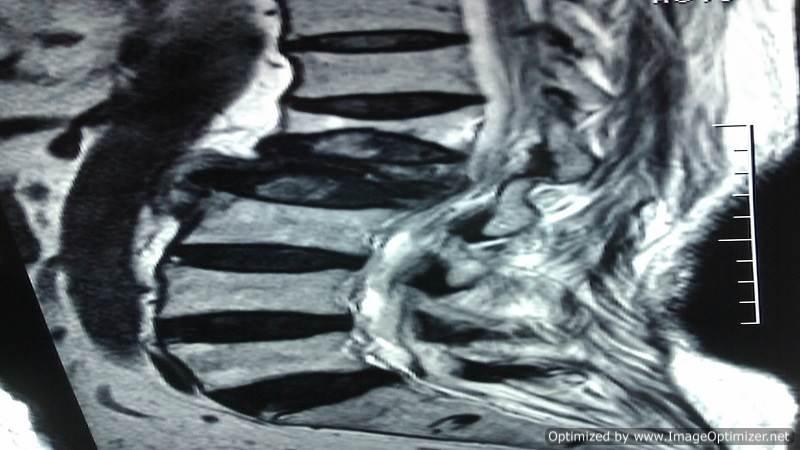
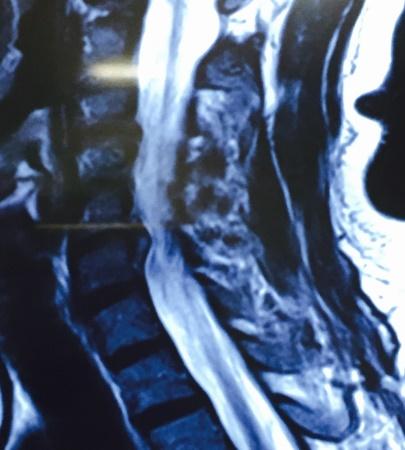
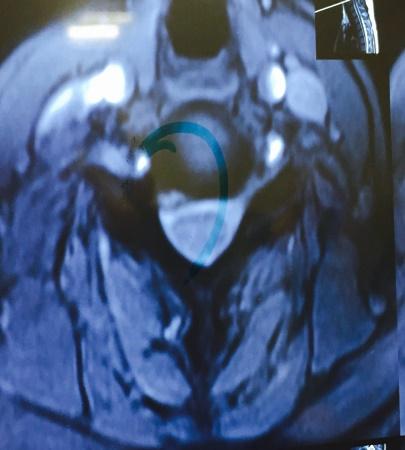
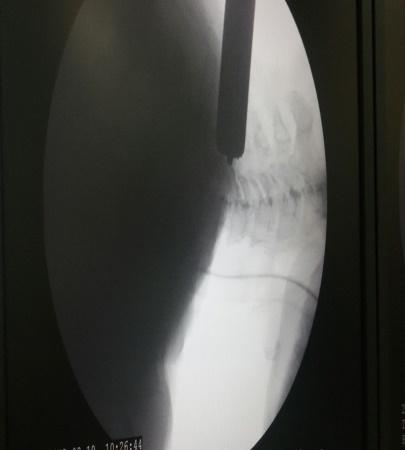
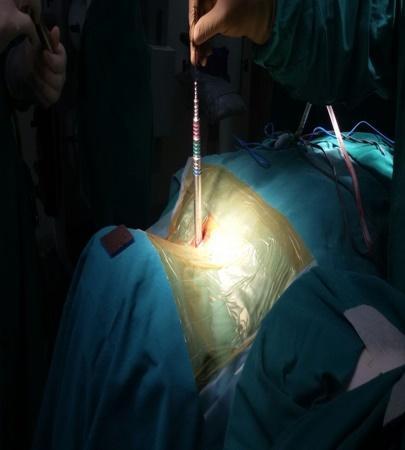
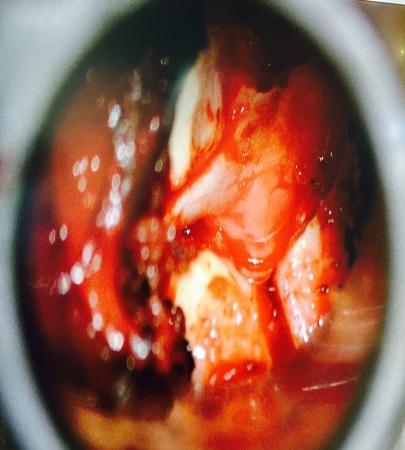
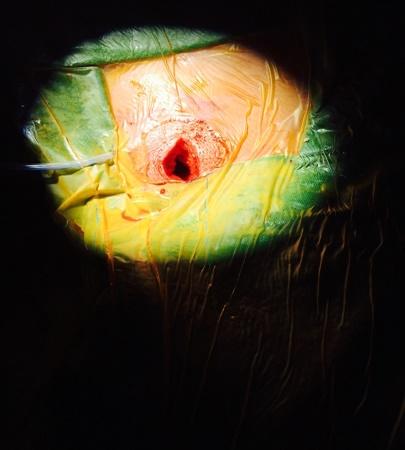
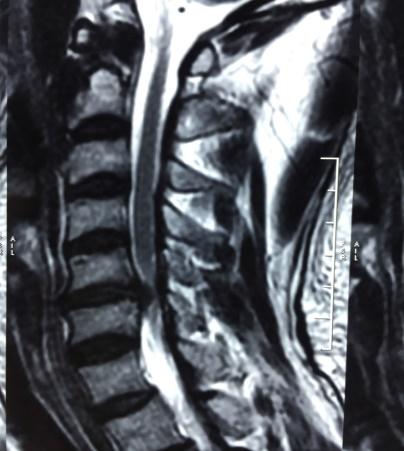
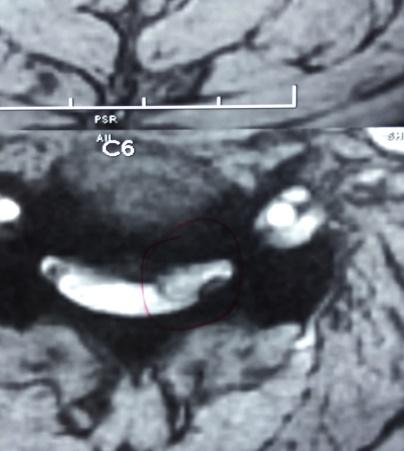
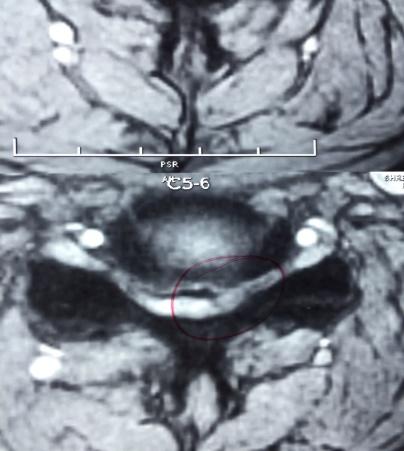
Micro Endoscopic Cervical Discectomy (MECD)
MECD is a minimally invasive technique designed for cervical spine surgery, offering effective treatment for cervical disc prolapse and related conditions.
Key Features of MECD:
- Selective application: Ideal for cervical disc prolapse and root canal stenosis.
- Muscle-splitting approach: Performed with serial dilators and a Metrx Tube, using a microscope or RIWO system for enhanced precision.
- Micro-foraminotomy: Removes pressure from the affected nerve root with targeted precision.
- Small incision: Only 1.5 cm, reducing scarring and healing time.
- Preservation of paraspinal muscles: Maintains normal anatomy and reduces post-operative discomfort.
- Minimal blood loss: Enhances safety and recovery.
- Immediate mobilization: Patients can move soon after surgery.
- Short hospital stay: Typically 2 days.
- Disc preservation: Normal discs are preserved, avoiding the need for fusion surgery when possible.
Note:- All images are copyrighted and require proper licensing or permission for use. Unauthorized use is prohibited.
Note:- All images are copyrighted and require proper licensing or permission for use. Unauthorized use is prohibited.
Note:- All images are copyrighted and require proper licensing or permission for use. Unauthorized use is prohibited.
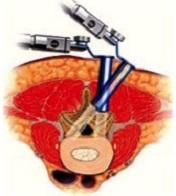
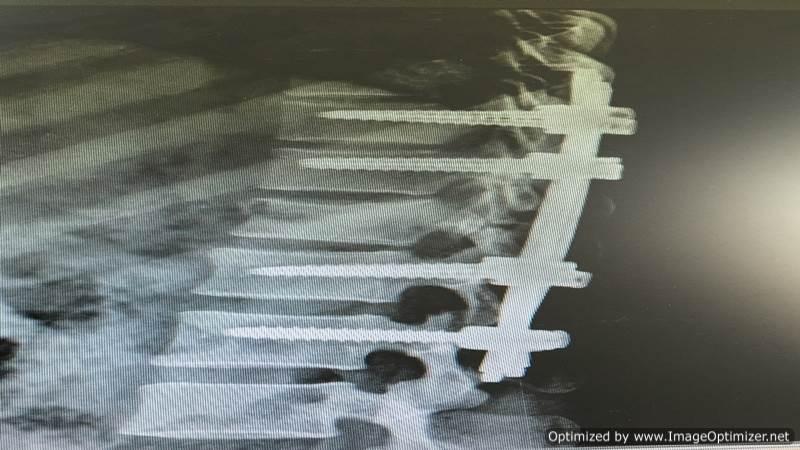
Percutaneous Transpedicular Stabilization
Advantages of Percutaneous Pedicle Screws:
- Muscle preservation: Ensures minimal disruption to the surrounding tissues.
- Stabilization of vertebrae: Provides effective support and alignment.
Procedure Highlights:
- Multiple tiny stab incisions: Used for pedicle screw and rod insertion.
- 3-D C-arm/O-arm guided procedure: Ensures precision and safety.
- Paraspinal muscle preservation: Maintains muscle integrity.
- Immediate mobilization: Promotes faster recovery.
- Versatility: Useful for treating traumatic or osteoporotic spinal fractures, as well as spine deformity correction.
Additional Note:
- When indicated, I perform minimally invasive percutaneous pedicle screw fixation/stabilization, ensuring optimal outcomes with reduced recovery time.
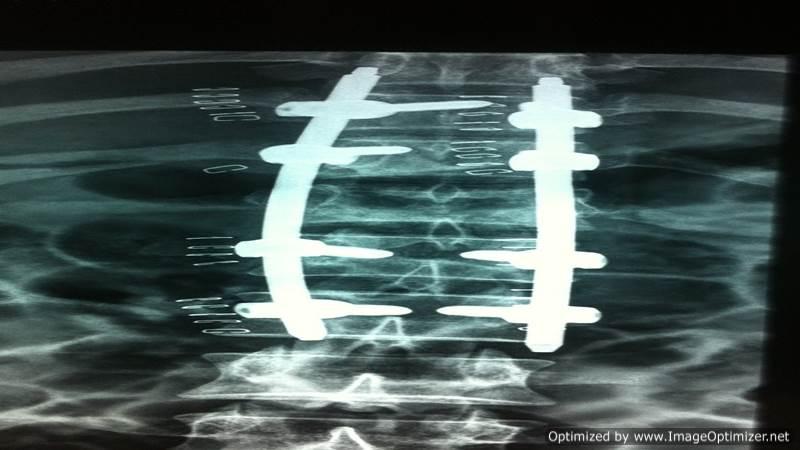
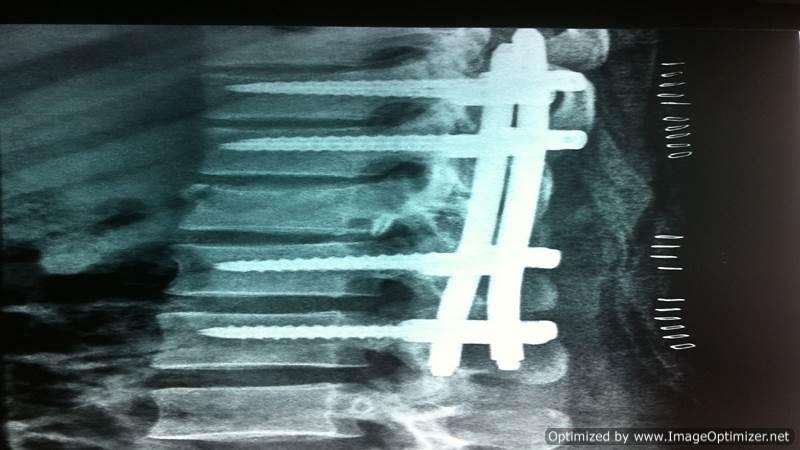
Note:- All images are copyrighted and require proper licensing or permission for use. Unauthorized use is prohibited.
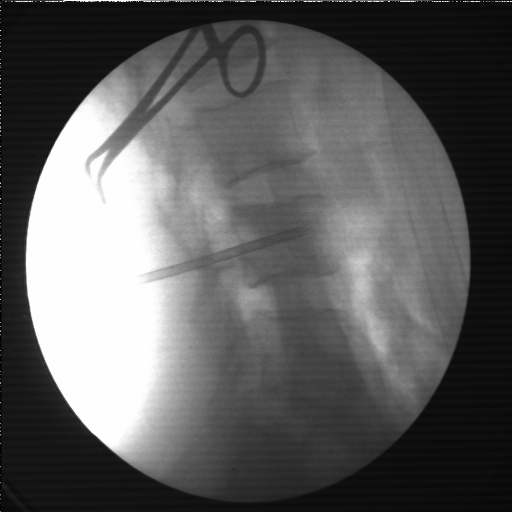
Percutaneous Spinal Biopsy
Using the same technique as vertebroplasty, a spinal vertebral body biopsy can be performed. This minimally invasive procedure is carried out under local anesthesia, ensuring patient comfort and safety.
Note:- All images are copyrighted and require proper licensing or permission for use. Unauthorized use is prohibited.
Note:- All images are copyrighted and require proper licensing or permission for use. Unauthorized use is prohibited.
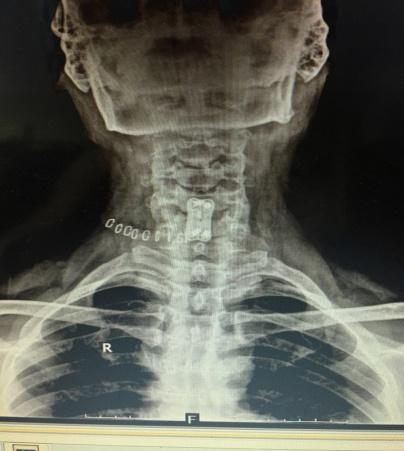
Cervical Spine Surgery
I frequently perform cervical spine surgeries for conditions such as cervical disc prolapse, cervical myelopathy, cervical trauma, and unstable cervical spine disorders, utilizing the principles of minimally invasive spine surgery (MISS) to ensure better outcomes with minimal discomfort.
Anterior Cervical Fusion / Foraminotomy:
- Effective for spondylosis and radiculopathy.
- Performed using an operating microscope for enhanced precision.
- Small incision ensures minimal scarring.
- Negligible blood loss for improved patient safety.
- Quick recovery: Patients are typically discharged on Day 2 or Day 3.
Cervical Posterior Decompression
- Recommended for OPLL (ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament) and cervical canal stenosis.
- Can be performed with or without lateral mass screw fixation, based on the patient’s condition.
- Short hospital stay: Discharge within 4 to 5 days.
Note:- All images are copyrighted and require proper licensing or permission for use. Unauthorized use is prohibited.

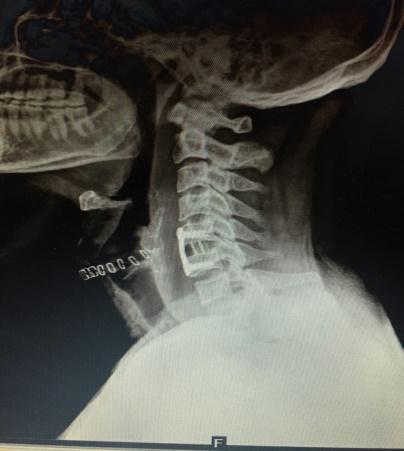
Note:- All images are copyrighted and require proper licensing or permission for use. Unauthorized use is prohibited.
Contact us
Don't Hesitate Contact us for any Information
Call us to this number for immediate support
